Impact driving and vibrating are trenchless technologies based on setting foundation, bracing and sealing components into soil using either impact driving rigs or vibrators. These technologies are both very effective, imposing minimal requirements on constructional readiness. Their advantages include low impact on the surrounding environment, the possibility of carrying out less complex foundation constructions in complicated foundation conditions and last but not least the possibility of subsequent simple removal of both temporary sheeting constructions after the construction works are finished as well as permanent constructions after the construction lifetime is over. The vibrating technology is primarily used in non-cohesive soils. Vibrators loosely hung up on a carrier are the most commonly used types. Depending on local geological conditions and the vibrating components size it is possible to choose among several high-performance vibrators to ensure an optimal development of vibrating processes.Vibrating can also be used in developed areas where high-frequency vibrators have to be used to minimise negative impacts of vibrations on surrounding subjects.
The technology of impact driving is especially used for penetrating elements into settled non-cohesive and cohesive foundation soils or for penetrating elements into semi-solid rock. Diesel or hydraulic impact drilling rigs are fitted either at the crane leader or they are free hung on the crane hinge.
 Common depths achieved in our geological conditions with vibrating or driven components range between 6 to 12 m, however,if an appropriate mechanism is chosen, depths of over20 m can be also reached.The choice of a suitable mechanism and the type of a foundation component for a specific construction needs to be consulted with a company geotechnician, whose task is to recommend the most suitable driving or vibrating procedure based either on a geological investigation, or possibly on a penetration test. The penetration test provides the best results among all investigation methods used, describing the most probable process of driving.
Common depths achieved in our geological conditions with vibrating or driven components range between 6 to 12 m, however,if an appropriate mechanism is chosen, depths of over20 m can be also reached.The choice of a suitable mechanism and the type of a foundation component for a specific construction needs to be consulted with a company geotechnician, whose task is to recommend the most suitable driving or vibrating procedure based either on a geological investigation, or possibly on a penetration test. The penetration test provides the best results among all investigation methods used, describing the most probable process of driving.
Bearing foundation components are used for transferring load from a building construction to a more bearable subsoil layer. All the mentioned advantages of driving technologies are fully exploited here - a component is fitted and the surrounding soil is concurrently compacted, resulting in its improved geotechnical properties. Foundation components carried out in this way can be further used as standard piles. Reinforced concrete driven piles either with a square pattern and a dimension of 30×30 cm up to 40 (45)×40 (45) cm or a circular pattern up to 60 cm in diameter can be used for these purposes. They provide for a reliable foundation of buildings in less bearing foundation soils. Steel piles driven either at a time (steel pipes, weldings), or gradually (from wall components - sheet piles) can also be used. The method of driving and vibrating can also be used for carrying out gravel and soil piers (See the chapter on Improving foundation soils with the method of vibroflotation).
Sheeting constructions are used for sheeting foundation pits, excavated material and in fillings. Vibrated or rammed sheet pile walls are mainly used here, as they have, besides their sheeting function, a sealing function in the process of realisation of foundation pits below groundwater level. In cases of dry pits it is possible to use so called (Berliner) rider walls with rammed or vibrated riders.
Sealing constructions are used for sealing a specific area against ground water seepages. These are either temporary constructions used for sealing of foundation pits or, on the contrary, permanent constructions preventing leakage of contaminated ground water from a specific closed area (old landfills, environmentally burdened areas in places with closed production etc.). These constructions can possibly use sheet pile walls or so called thin cut-off walls (see chapter Diaphragm walls) also carried out with the use of the vibrating technology.
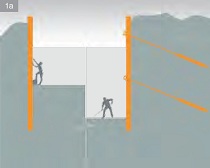
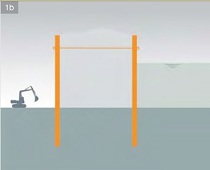
Different methods of using constructions made of rammed or vibrated components
1a) sheeting of a foundation pit with a cantilever or an anchored sheet pile wall
1b) sheeting of a foundation pit in a river with a double cofferdam made of sheet pile walls coupled with draw-bars
1c) sheeting of an excavation with braced sheet-pile walls