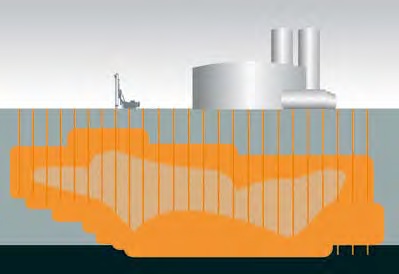
» to prevent spreading of pollutants through underground water and soil bodies with the help of vertical barriers;
» to close a pollution deposit with the combination of horizontal and vertical barriers;
» to immobilize pollutants through solidification;
» to create a hydraulic barrier or drainage system for pumping and drainage of polluted underground water;
» to increase serviceable area of landfills for communal and other types of waste through dynamic compaction.
| Cut-off wall | Composite cut-off wall (with a membrane) |
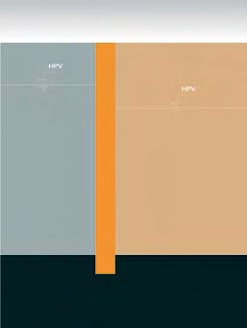 |  |
 Diaphragm cut-off walls create a vertical barrier that can quickly and effectively prevent spreading of pollutants. Special mineral substances with a low coefficient of transmission (k<10-10 m/s) are used as a sealing filling; special materials with high resistance to corrosion and the ability to absorb heavy metals (Zeofix™, Sekofix™) are applied in aggressive environments. In extremely loaded localities with high aggressiveness of the environment it is possible to use a diaphragm cut-off wall with a geomembrane - inserted PEHD foil of 1,5 to 3,0 mm of thickness - connected with special locks. Guaranteed impermeability of a sealing system created in this way reaches up to k = 10-15 m/s. In suitable geological conditions it is possible to use thin cut-off walls as a vertical sealing component - one-line or multiple-line vibrated and injected walls of 10 to 15 cm of thickness (see chapter Diaphragm walls). Thin cut-off walls are suitable for reduction of see pages in sandy soils in combination with active water pumping. Diaphragm walls with reactive membranes that contain a special filling absorbing pollutants or decomposing pollutants to harmless substances represent the most modern technology of underground water maintenance. This technology is especially effective for the maintenance of waters polluted by CIU(chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons), which now list among the most common pollutants of rock environment.
Diaphragm cut-off walls create a vertical barrier that can quickly and effectively prevent spreading of pollutants. Special mineral substances with a low coefficient of transmission (k<10-10 m/s) are used as a sealing filling; special materials with high resistance to corrosion and the ability to absorb heavy metals (Zeofix™, Sekofix™) are applied in aggressive environments. In extremely loaded localities with high aggressiveness of the environment it is possible to use a diaphragm cut-off wall with a geomembrane - inserted PEHD foil of 1,5 to 3,0 mm of thickness - connected with special locks. Guaranteed impermeability of a sealing system created in this way reaches up to k = 10-15 m/s. In suitable geological conditions it is possible to use thin cut-off walls as a vertical sealing component - one-line or multiple-line vibrated and injected walls of 10 to 15 cm of thickness (see chapter Diaphragm walls). Thin cut-off walls are suitable for reduction of see pages in sandy soils in combination with active water pumping. Diaphragm walls with reactive membranes that contain a special filling absorbing pollutants or decomposing pollutants to harmless substances represent the most modern technology of underground water maintenance. This technology is especially effective for the maintenance of waters polluted by CIU(chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons), which now list among the most common pollutants of rock environment.
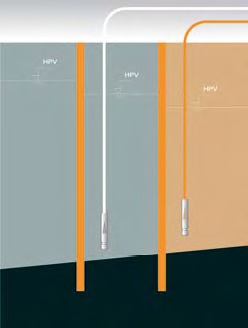
Thin cut-off walls
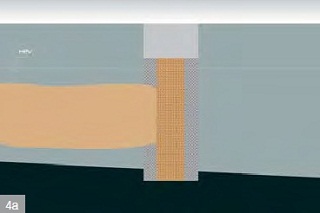
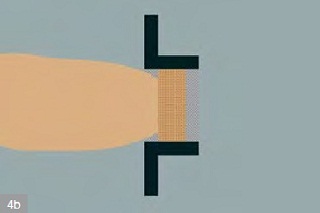
| Reactive diaphragm wall 4a) vertical profile 4b) lay-out - funnel-and-gate system | |
 |  |
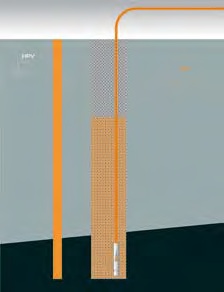
 In less accessible places where it is not possible to carry out a standard diaphragm cut-off wall a grout curtain can be used - a vertical or inclined sealing component created from two or more lines of standard grouting or jet-grouting, again with the possibility of using special sealing materials. Grouting is useful for final sealing of rifts in rock massifs; jet-grouting can also be used to create a horizontal sealing layer in the subsoil. Other uses of grouting also include solidification of contaminated soils - grouting through the polluted material or material with unsuitable properties with a whole some binder creates a chemically inert compact material closing the pollutant inside. Solidification is suitable for the maintenance of permeable soils polluted with heavy metals both above and under the underground water level, for immobilizing ashes from power stations, for stabilisation of chemical and other waste sludges, etc.
In less accessible places where it is not possible to carry out a standard diaphragm cut-off wall a grout curtain can be used - a vertical or inclined sealing component created from two or more lines of standard grouting or jet-grouting, again with the possibility of using special sealing materials. Grouting is useful for final sealing of rifts in rock massifs; jet-grouting can also be used to create a horizontal sealing layer in the subsoil. Other uses of grouting also include solidification of contaminated soils - grouting through the polluted material or material with unsuitable properties with a whole some binder creates a chemically inert compact material closing the pollutant inside. Solidification is suitable for the maintenance of permeable soils polluted with heavy metals both above and under the underground water level, for immobilizing ashes from power stations, for stabilisation of chemical and other waste sludges, etc.
Vertical and horizontal sealing element made by jet grouting

Solidification by grouting (classic, jet grouting)
| Underground (French) drain | Underground drain with a membrane (one-side) |
 |  |
Underground one side drain with a cut-off wall

Hydraulic barriers create passive (drains) or active (pumped wells) obstructions to further spreading of pollutants dissolvedor dispersed in underground water, floating on its surface or moving around on the basis of permeable collectors.
Drainage diaphragm walls (vertical drain, French drain) capture contaminated water that is deflected down to pumping shafts. The trench is excavated under a protection of standard sheeting, sheet pile walls or special degradation slurry. Drainage filling is formed by gravel, or possibly by laying drainage perforated pipes to the bottom. Depending on the arrangement, a drain age wall can contract water reciprocally or just one-sidedly (incombination with a diaphragm cut-off wall or inserted sealing geomembrane). Active hydraulic curtain consists of a line of pumping drillholes (wells) with overlapping drawdown cones. Pumped water is drained for decontamination. Some landfills, especially those of communal waste, can be characterised by their low level of compaction.
 The volume of landfilled waste can be decreased by several tens of percents through the use of dynamic compaction with a desk of up to 18 tons of weight or high-performance vibration compactors. The compaction not only increases the capacity of a landfill, but also prevents uncontrollable subsidence of the surface of landfills, which lowers the possibility of damage inflicted on the covering insulation layers.
The volume of landfilled waste can be decreased by several tens of percents through the use of dynamic compaction with a desk of up to 18 tons of weight or high-performance vibration compactors. The compaction not only increases the capacity of a landfill, but also prevents uncontrollable subsidence of the surface of landfills, which lowers the possibility of damage inflicted on the covering insulation layers.
All the technologies mentioned above are offered by the Zakládání staveb, Co., including realisation of exploration works, elaboration of a feasibility study, consultancy and supply of project realisation documentation. Sanitation of contaminated areas, soil and water protection are an interdisciplinary issue.There fore the company co-operates with both expert companies and research places in our country as well as within the international scope.
| Dynamic compaction of a dump material | Sanitation, building of landfills |
 |  |