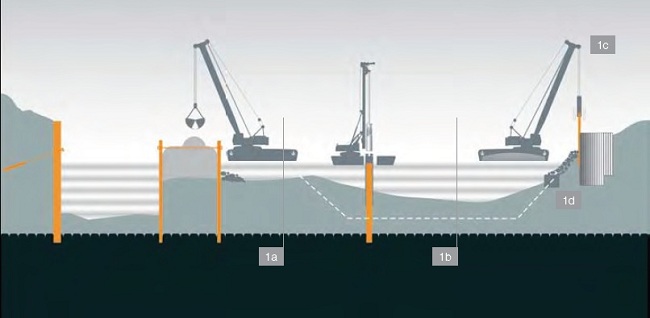
Examples of different types of constructions carried out from the water surface
1a) securing a foundation pit with an anchored sheet-pile or diaphragm wall and
a doublewalled cofferdam made of sheet-pile walls coupled with draw-bars together
with simultaneous dredging of a river-bed for the shipway,
1b) pile drilling from a naval mechanism into the river-bed,
1c) driving of sheet-pile walls from a naval mechanism, e.g. for embankment walls
or cofferdamsfor bridge foundations,
1d) bank strengthening made of quarry stone.
Almost all of the technologies of special foundation engineering carried out by the Zakládání staveb, Co., can be applied at the works of water resources engineering. However, the most commonly used is the technology of sheet pile driving and vibrating. It is either applied to temporary constructions, as for example:
» Single-row or double-row sheet pile cofferdams used for sheeting and providing protection for foundation pits carried out either close to or directly in the watercourse;
» Piers in rivers used as supporting bearing structures when both new and old bridges or similar constructions over watercourses are built or reconstructed;
or as a permanent part of the water works:
» quay edges built as sheet pile bulkheads;
» mooring dolphins in ports formed by several driven steel piles or steel piles fitted into a prebored hole;
» crush barriers at bridge pillars and navigation lock entries providing protection for concrete pillar structures and gates of navigation locks as well as for securing safe navigation on surrounding water ways;
» cut-off walls aprons at river dams and fill barriers forming a water tight screen under the weir or dam body; this screen prevents undesirable waterflow within the subsoil causing suffusion that could potentially result in the waterwork destruction.
Apart from these works connected with the technologies of driving and vibrating the Zakládání staveb, Co., carries out other specific technologies especially applied to the following water resources engineering constructions:
 Construction of hydropower plants - securing a foundation pit of the power plant under construction using sheet pile walls, diaphragm walls and pile walls, jet grouting and anchoring, underpinning the existing weir body structure, carrying out drainages and pumping wells, foundation of the small water plant building;
Construction of hydropower plants - securing a foundation pit of the power plant under construction using sheet pile walls, diaphragm walls and pile walls, jet grouting and anchoring, underpinning the existing weir body structure, carrying out drainages and pumping wells, foundation of the small water plant building;
Reconstructions of ports - carrying out new port walls with anchored sheet-pile walls or prefabricated diaphragm walls, carrying out pile sleeves and crush barriers, dredging and cleaning of docks;
Reconstructions of navigation locks - securing foundation pits in close proximity of watercourses with the common use of sheet pile walls, diaphragm walls, pile walls, jet grouting and anchoring. Other works include underpinning of the existing weir stucture, drainages and pumping wells, foundation of the navigation lock structure, changing the dam structure of then avigation lock or building a turn out in the shipway;
Reconstructions of weirs - securing a dry pit in the riverbed, underpinning or carrying out a new weir foundation, reconstructions of particular weir sections, repairs or changes of dam structures (e. g. weir gates);
Anti-flood protection measures - carrying out anti-flood fill barrier including a sealing core made of sheet pile walls or clay cut-off walls. The bottom part of mobile barriers can be carried out with diaphragm walls, jet grouting or sheet pile walls;
 Other types of waterworks - corrections of river banks, revetment of river banks with paving and shivers, stone backfills to protect weir or bridge piers, sanitation of riverbed erosions;
Other types of waterworks - corrections of river banks, revetment of river banks with paving and shivers, stone backfills to protect weir or bridge piers, sanitation of riverbed erosions;
Material-pipes siphons - providing a complete delivery of siphons carried out with the technology of floating and setting or possibly driving into a trench. The complete works include excavation of a trench in the river-bed, assembly at the river bank, sinking, floating and setting the siphon into the river-bed trench (or possibly its retraction) until the siphons are connected to bank cofferrdams, backward fillings in the river-bed carried out and the bed and banks protected with stone filling;
Setting cable siphons - a complete delivery starting with assembly, going on with driving into the trench, connecting and final treatment of the riverbed to achieve its original condition;
Excavation of trenches in other watercourse underpasses- e.g. for a retracted underground tube - including building of a dry dock, carrying out riverbank cofferdams with diaphragm walls, retreatment of the river-bed to achieve the original shape and strengthening banks with pavings and stone backfills;
Dredgings of river-beds - removal of river drifts from the shipways in watercourses. The excavation is carried out with naval mechanisms, materials transported to land fills or tranship centres;
Cleaning storage tanks, disposal of sludges - excavation of old sediments in storage tanks consists in removal of sludges from waterworks kept in retention tanks with the use of naval mechanisms, transport and appropriate disposal of sludges.